Editor's Notes:
Under the stress of this COVID-19 pandemic, physicians around the world are struggling on finding the plan for prevention and treatment of COVID-19. In Shanghai, all the diagnosed COVID-19 cases go to Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center. Since Jan 2020, the expert physicians in Shanghai have taken care of 371 cases and most of these patients recovered. The Shanghai experts have accumulated tremendous experiences and knowledge. We would like to share one lecture with all the physicians around the world. Together we can beat the virus.
The speaker Professor Hu Bijie is a member of the Shanghai Combined Task Force on COVID-19. He is also the chief of Department of Infectious Disease and chief of Department of Infection Control of Zhongshan hospital affiliated to Shanghai Fudan University.
COVID-19 has caused many death and critical cases all over the world. "Shanghai Plan" has focused on risk assessment, prognosis prediction, and combination therapy for early intervention to prevent the development of severe cases. According to Professor Hu among all the medications used, Hydroxychloroquine was found to effectively and safely prevent the progression of disease and minimize the numbers of severe and critical patients. The fact is new severe and critical COVID-19 cases in Shanghai have decreased significantly since February 5th, suggesting Hydroxychloroquine might be one of the correct medications to reverse this pandemic.
Considering the strategic value of prevention and intervention of severe COVID-19 cases, we believe that the initial observational data from Shanghai might provide reference for physicians around the world although the effectiveness and safety of the Hydroxychloroquine in the "Shanghai Plan" needs to be further evaluated through randomized control studies.
COVID-19 is one of the most challenging pandemic diseases in the history of modern medicine. We are seeing a little ray of hope now and with the joint efforts from all over the world, it is believed that this pandemic will soon hit a turning point.
Dr. Kathy Shi, MD, Ph.D,
CEO, SinoUnited Health
The Shanghai epidemic prevention and control press conference said: Hydroxychloroquine ranked as the first drug in "Shanghai Plan" therapeutic drugs, Shanghai's experience in diagnosing and treating COVID-19 is worth sharing. Up until March 15, the clinical study of Hydroxychloroquine in treating COVID-19 has enrolled a total of 184 cases, involving 21 hospitals. The preliminary results showed that the Hydroxychloroquine treatment was effective and safer. Just yesterday, Trump announced that Hydroxychloroquine and Remdesivir have been approved by the FDA for special use.
Hydroxychloroquine might be the "special medication", the hope for the public, to reverse the pandemic trend of COVID-19 for real. The scale of the COVID-19 being so large and the impact being so deep, we haven't seen something like this for hundreds years. This outbreak has made us realize that the world is closely connected; no country can be alone; and no one can live without another. Only by working together can we beat the virus.
Following is summary of Pro. Bijie Hu's report on COVID-19. The discussions is based on Chinese National Health Commission Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol (Trial Version 7) and on the consensus of the Shanghai Combined Task Force on COVID-19.
Content:
Early detection and prevention of deterioration of COVID-19 Pneumonia
Antiviral treatment and applications
Corticosteroid and antibiotic applications
Maintenance and support of the immune system
Management of Severe Pneumonia and Critical Pneumonia
Diagnostic criteria for COVID-19 Pneumonia
Discharge criteria and RT-PCR re-test positivity
Here in Shanghai, we take the treatment measures of concentrate patients, concentrate experts and concentrate resources to treat COVID-19. We collect all adult cases and collectively put them in Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center for treatment. A total of 300 plus cases were treated.
These cases belong to "Severe Pneumonia" category, they need close clinical monitoring. In recent period, the ratio of severe pneumonia among COVID-19 diagnosed cases has almost diminished to zero. The reason for this result was due to our cumulative experiences in the effective treatment modalities and the application to clinical use. On daily basis, we go through each case as we treat and review their possible clinical & laboratory indicators that would indicate impending deterioration. We have to double our efforts to prevent the occurrence of severe clinical situations. If we could successfully prevent the occurrence of severe cases, we could conserve our medical resources significantly.
We have been able to sort out the early alarm indicators for severe COVID-19 pneumonia.
Clinical Indicators for deterioration of COVID-19 Pneumonia
Advanced age( age> 65y/o)
Complicated with other systemic diseases: diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, hypertension, obesity
Progressive worsening of lung parenchymal pathology > 50% for 2-3 days
CD4+ T lymphocytes number < 250/uL
Significant increase in serum IL-6 level
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) level > 2x normal range upper limit
Serum Lactic Acid >/= 3 mmol/L, with metabolic alkalosis
Major systematic diseases/old age -- a very important indicator/rapid progression of clinical symptoms and signs are the major factors. In addition, Shanghai team was the earliest group that took notice that CD4+ T cells subgroups are also very important severe disease early indicators.
CD4+ cut off value is probably at 250/μL, it is less likely to see severe cases with CD4>400/μL, CT scan of the chest with CD4>2000/μL cases almost showed no pathological findings. Here is a patient with progressive dropping of CD4+ level, reflecting its's clinical severity.
CD4+ and COVID-19 infections have close relationship. We are not sure the exact cause-effect of the two. There is a possibility that the virus specifically attack CD4+, caused CD4 level to drop significantly, therefore severely destroyed the immune system. There is also a relationship with the CD4+ cell count and the timing of viral shedding. The lower the CD4 count, the longer the viral shedding period.
Combined Approaches toward Prevention of Disease Progression(Mild cases and Common cases):
Antiviral drugs
Oxygen Therapy and supplementation/ Oxygen saturation monitoring
Maintenance of Immune system: Medications, Sleep, Mood management
Enhance supportive care, guarantee adequate caloric intake
Focusing on water & electrolyte balance, maintenance homeostasis.
Avoidance of antibiotics and glucocorticoids.
Anticoagulants and large dose of Vitamin C
First of all, we are focusing on antiviral drugs, Oxygen Therapy and supplementation/Oxygen saturation monitoring, Maintenance of Immune system: Some patients have high anxieties, we have also been focusing in the easing of their stress & terror and try to maintain and provide a good sleep quality routine.
We are also concerned about maintenance of patients' energy level, keeping a stable environment. We have also noticed that large quantity of Vitamin C (10-20 gram daily) use seemed beneficial.
In regard to the use of antiviral drugs, anti-HIV medication Lopinavir/Ritonavir, and a broad spectrum anti-viral drug, Abitor, the overall result compared to placebo group showed no significant difference. We, clinical physicians, felt that Arbitor has a slightly better response than Lopinavir/Ritonavir. One reason is that Lopinavir/Ritonavir has caused toxic side effects onto some patients, with severe GI reactions and further reduce patients' immune responses.
We, the Shanghai COVID-19 special medical task force members have a stronger and stronger believe that Hydroxychloroquine could be a good choice.After patients' use of Hydroxychloroquine, The number of our patient's clinical progression from "mild" class to "severe" class and from "severe" to "critical" class have been significantly reduced. Furthermore, the side effects of Hydroxychloroquine has not been as severe as we had imagined.
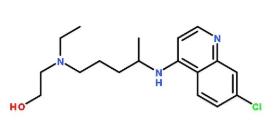
Some experts suggest that among the family of chloroquines, the toxic side effect of Hydroxychloroquine is quite low. We have been using the maximum dose as per manufacturer's insert, 400mg QD. We have also consulted with rheumatology experts, they agree that Hydroxychloroquine is comparatively safe to use in a normal situations.
Therefore, the recommended medications in our Shanghai COVID-19 medical treatment guidelines was quite simple. Besides Hydroxychloroquine, there are also National treatment guidelines' recommended Chloroquine Phosphate, Arbitor and Interfron. Some people have questioned us as to why we do not recommend more drugs to use. The reason is that we truly felt Hydroxychloroquine is the specific drug of choice for COVID-19.
We have compared Phase I epidemic period and Phase II epidemic period patient outcomes. In Phase I period, there were high ratio of severe cases and critical cases. In Phase II period (admission after Feb 5th), There is a significant drop in the number of severe cases and critical cases, we have attributed this outcome to our extensive use of Hydroxychloroquine. We have basically reached our conclusion on this finding.
The usage of glucocorticoid and antibiotic drugs have been tightly restricted for COVID-19 patients in Shanghai. Experts have different opinions about the usage of glucocorticoid. But one uniform consensus had been reached that if it is to be used, only small dosage and short-term application should be applied.
Data showed that a group of patients who had use glucocorticoid, their viral shedding time were prolonged. We have also observed that thee group of patients who had used glucocorticoid, their nasopharyngeal swab viral shedding time compared to non-users were 15 days vs 8 days. Stool nucleic acid shedding time were also prolonged. Steroid-user vs non-users were 20 days vs 11 days. Therefore, we should refrain from the urge to use steroid.
With Hydroxychloroquine treatment, the use of antibiotics were significantly reduced. According to statistics, our "mild" case patients needed much less antibiotic drugs with our knowledge of the disease nature. We have boldly discontinued all the use of antibiotics. The result has been satisfactory.
For maintenance and support of patient's immune system functions, we propose the use of Thymosin in some cases, it has shown beneficial results, especially in patients with low CD4+ and younger age group in early stage use shown more obvious beneficial effects.
On the other hand, we had used gamma-Globulin in Phase I period, but in Phase II period, we have stopped it's usage. In theory and combined with our present experiences, gamma-Globulin effect is limited.
In the management of severe and critical pneumonia cases, we have 5 teams consist of 5 ICU experts. We have been using advanced technology and now treatment modalities. (I will skip this topic here.) For those patients who continue to shed virus, we used plasma extracted from convalescent patients and transfused to these patients. We are having some hope for this therapeutic approach.

Indeed, some patients presented with negative RT-PCR test results at convalescent stage, but later, turned positive again in 3 days. For this, we have to be cautious and we have to accumulate more experiences before putting it into routine use.
For the diagnostic Criteria for COVID-19 pneumonia, which is more important? Laboratory findings or Clinical findings?
Actually, we found that the clinical presentations of respiratory symptoms and fever are not that significant. These symptoms are not specific enough for us to detect it early in its highly infectious phase. On the other hand, Chest CT scan has more specificity for COVID -19. RT-PCR testing does present with false negative results. For Chest CT scan, we need to learn more and we must avoid accidentally omitting cases with typical findings.
Cases that are definitely not COVID-19, we must have the confidence to exclude them. As for serum findings, in Shanghai, this is now added as a supplementary tool to the diagnosis of this viral disease. At current stage, it is a worthwhile direction for further development. But the stability and reliability of the test kits --false-positive, false-negative--issues are not solved yet. In addition, the serum tests can only give qualitative, not quantitative results. We still need to work more and accumulate more experiences on these technical issues before its widespread use.
In our clinical practices, in epidemiological studies, with the findings of respiratory symptoms and signs, with the findings of disease toxicity, with chest imaging findings, with RT-PCR findings, with specific antibody testing and monitoring, how do we make the final diagnosis for COVID-19 ? Under different circumstances, some we could be sure, but some still needs further considerations.
National Guidelines for Discharge from Hospitals:
Normal body temperature for 3 consecutive days
Significant improvement with respiratory symptoms
Chest imaging studies showed significant improvement compared with acute stage findings.
Two consecutive negative results from respiratory tract secretion swabs ( sampling must be 24 hours apart)
Shanghai: After two consecutive negative respiratory secretion swabs, stool sample must also show negative viral nucleic acid test result.
Shanghai: entire illness course > 2 weeks.
As noted, our Shanghai COVID-19 Hospital Discharge Criteria has two additional requirements compared to National COVID-19 Hospital Discharge Criteria
The reasons for these additional requirements are based on the following:After two consecutive respiratory tract secretion swab tested negative, we are also looking for stool specimen testing negative. Shanghai team experts have postulated that if after 4 weeks of positive stool results, the possibility of COVID-19 contagiousness through feces to others are low. Obviously, we still need further data to support this. We do allow patients to be discharged, but we give instructions as to how to handle their excretions after returning back to the community.
Illness duration exceed 2 weeks before discharge—we postulate that most of viral infections are still contagious within 2 weeks, after 2 weeks, some viruses are self-limited and self-resolving, even without any medication. In Shanghai, Discharge orders are given with more strict requirements. Besides the two above listed criteria, we also require Task Force expert physicians to review patients' chest imaging films and confirm the resolution of the lung parenchymal pathologies prior to discharge.
After two consecutive negative respiratory secretion swabs, stool sample must also show negative viral nucleic acid test result. We have also accumulated the following experience: The viral shedding duration for respiratory tract secretion swab test is indeed different from the stool specimen. Viral shedding duration is much longer in stool compared to respiratory tract pathway.






